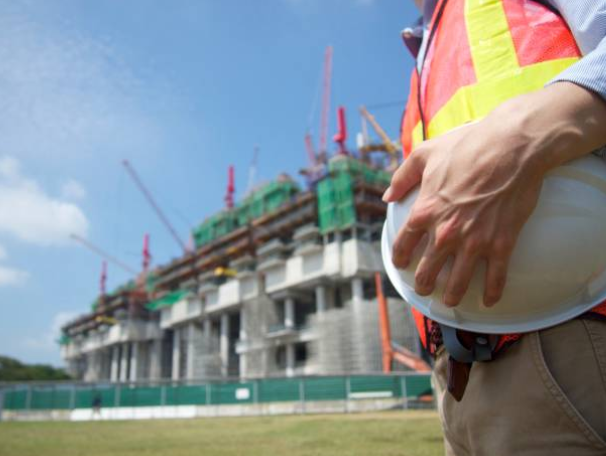
Secure your workplace in Singapore with comprehensive safety & health management systems. Ensuring well-being for all!
Comprehensive Safety and Health Management Systems (SHMS) represent an organized approach to safeguarding employees in any professional environment. These systems integrate policies, procedures, and practices aimed at identifying hazards, reducing risks, and maintaining the overall welfare of personnel. By embedding these frameworks into daily operations, organizations create workplaces that encourage efficiency, accountability, and a strong culture of care. Quality Safe ensures your business is compliant with the Safety and Health Management System regulations in Singapore, helping organizations implement these systems effectively.
Workplace wellness contributes significantly to productivity, employee engagement, and satisfaction. Companies that emphasize health and well-being see fewer absences, lower medical expenses, and stronger morale, which ultimately reflects in performance. By addressing physical, mental, and environmental factors affecting employees, organizations cultivate an environment where staff members feel valued and motivated.
Understanding Safety and Health Management Systems
Definition of Safety and Health Management Systems
Safety and Health Management Systems are structured programs that guide organizations in maintaining a safe and healthy workplace. These systems include a combination of strategies, from risk identification to preventive measures, ensuring that employees operate in secure conditions while complying with statutory regulations. They serve as a blueprint for continuous improvement, allowing businesses to respond to emerging challenges effectively.
Management’s Role in Workplace Safety
Management sets the standard for safety practices within an organization. Leadership involvement includes defining safety policies, organizing training initiatives, and creating a culture of awareness. Employees are more likely to adhere to safety measures when they see management actively engaged in protecting staff and addressing hazards systematically.
Components of a Safety and Health Management System
An effective SHMS encompasses several integral elements:
- Hazard identification: Recognizing potential risks across tasks and facilities.
- Risk assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified hazards.
- Training programs: Equipping employees with knowledge to handle risks safely.
- Safety policies: Clearly defined rules and protocols for safe operations.
- Performance monitoring: Tracking safety metrics and identifying areas for improvement.
- Emergency preparedness: Planning for unforeseen events to minimize damage and injury.
- Continuous improvement: Updating procedures in response to feedback, technological advances, and regulatory changes.
These components work together to create a system that adapts to evolving workplace demands while protecting employee health.
Workplace Safety and Health in Singapore
Current Scenario
Singapore maintains high standards of workplace safety, with structured initiatives guided by government agencies and industry practices. Regular inspections, reporting mechanisms, and industry collaboration have contributed to reducing occupational hazards. Accurate data reporting and evidence-based approaches provide clarity for policymakers and organizations aiming to improve safety outcomes.
Comparative Perspective
When compared with other developed nations, Singapore demonstrates a proactive stance toward occupational safety, often implementing regulations faster than regional peers. While approaches vary globally due to differences in infrastructure and labor practices, Singapore’s integrated system serves as a model for balancing economic efficiency with worker protection.
Factors Contributing to Workplace Issues
Several factors can contribute to workplace hazards, including outdated equipment, insufficient safety awareness, high operational pressures, and environmental risks. Recognizing the sources of these issues allows organizations to address underlying causes rather than focusing solely on symptoms. Through systematic risk reduction strategies, companies can minimize incidents and maintain a healthier workforce.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
Workplace Safety and Health Act (WSHA)
The Workplace Safety and Health Act establishes rules for maintaining employee safety across sectors. Its focus lies in preventing injuries, occupational illnesses, and ensuring staff are protected during their daily tasks. This regulatory framework provides businesses with clear expectations and accountability measures.
Ministry of Manpower’s Role
The Ministry of Manpower oversees compliance with safety standards, providing guidance, inspections, and enforcement where necessary. By supporting employers and employees, the ministry promotes fair and balanced practices while reducing occupational risks.
Repercussions of Non-Compliance
Organizations that fail to meet safety requirements face penalties such as fines, legal proceedings, reputational harm, and operational interruptions. Such outcomes can have long-lasting effects on both business performance and employee trust, highlighting the significance of adopting robust safety systems.
Advantages of Implementing SHMS
Structured safety systems contribute to a positive work environment by encouraging collaboration, communication, and proactive problem-solving. Employees feel more secure, which can increase engagement and job satisfaction. Implementing these measures also reduces workplace accidents, minimizes downtime, and protects organizational resources.
By creating safer workplaces, companies can improve efficiency and morale simultaneously. Staff members are more likely to participate in projects actively and maintain high levels of performance when they feel physically and mentally secure.
Steps for Implementation
Establishing an SHMS involves multiple stages: assessing current needs, defining objectives, allocating resources, and developing a detailed plan of action. Active participation from all levels of staff strengthens adoption, while monitoring and feedback loops help adjust strategies as necessary.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Organizations may encounter resistance to change, limited resources, or gaps in knowledge. Addressing these issues requires training, consistent communication, and engagement strategies that help employees understand the benefits of new systems. Clear leadership and continuous evaluation allow the transition to be smoother and more effective.
Role of Technology
Technological solutions assist in maintaining safety standards. These include monitoring devices, digital reporting tools, automated alerts, and telehealth services for immediate intervention. Technology can streamline safety management and provide actionable insights for risk prevention.

Case Studies
Organizations that have successfully adopted SHMS report improved operational efficiency, reduced incidents, and higher employee satisfaction. These examples demonstrate that structured safety programs are not only protective but also support growth, innovation, and long-term sustainability.
Looking Ahead
Future developments in workplace safety in Singapore may include updated regulations, enhanced reporting systems, and broader wellness initiatives. Progressive measures such as mental health programs, flexible arrangements, and employee engagement strategies reflect an evolving understanding of wellbeing at work.
By adapting to new standards and adopting comprehensive approaches, organizations can maintain safe, productive environments that attract talent and retain employees over the long term.
Conclusion
Safety and Health Management Systems in Singapore provide a structured pathway to maintaining employee well-being and operational efficiency. These systems combine preventive measures, training, monitoring, and leadership involvement to reduce risks and promote a secure workplace culture. With regulatory support, technological tools, and ongoing improvements, organizations can create environments where staff feel protected, motivated, and empowered to contribute effectively. Investing in these frameworks ultimately strengthens organizational performance while safeguarding the welfare of all employees.








































Leave a Reply